Introduction
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation, mostly in the digestive tract. It can bring intense discomfort, disrupt everyday life, and lead to serious complications. Although millions of people worldwide live with Crohn’s, there’s still no cure and its exact cause remains unclear. That said, recent research has given fresh hope, pointing toward better ways to treat and manage the condition in the future.
What is Crohn’s Disease?
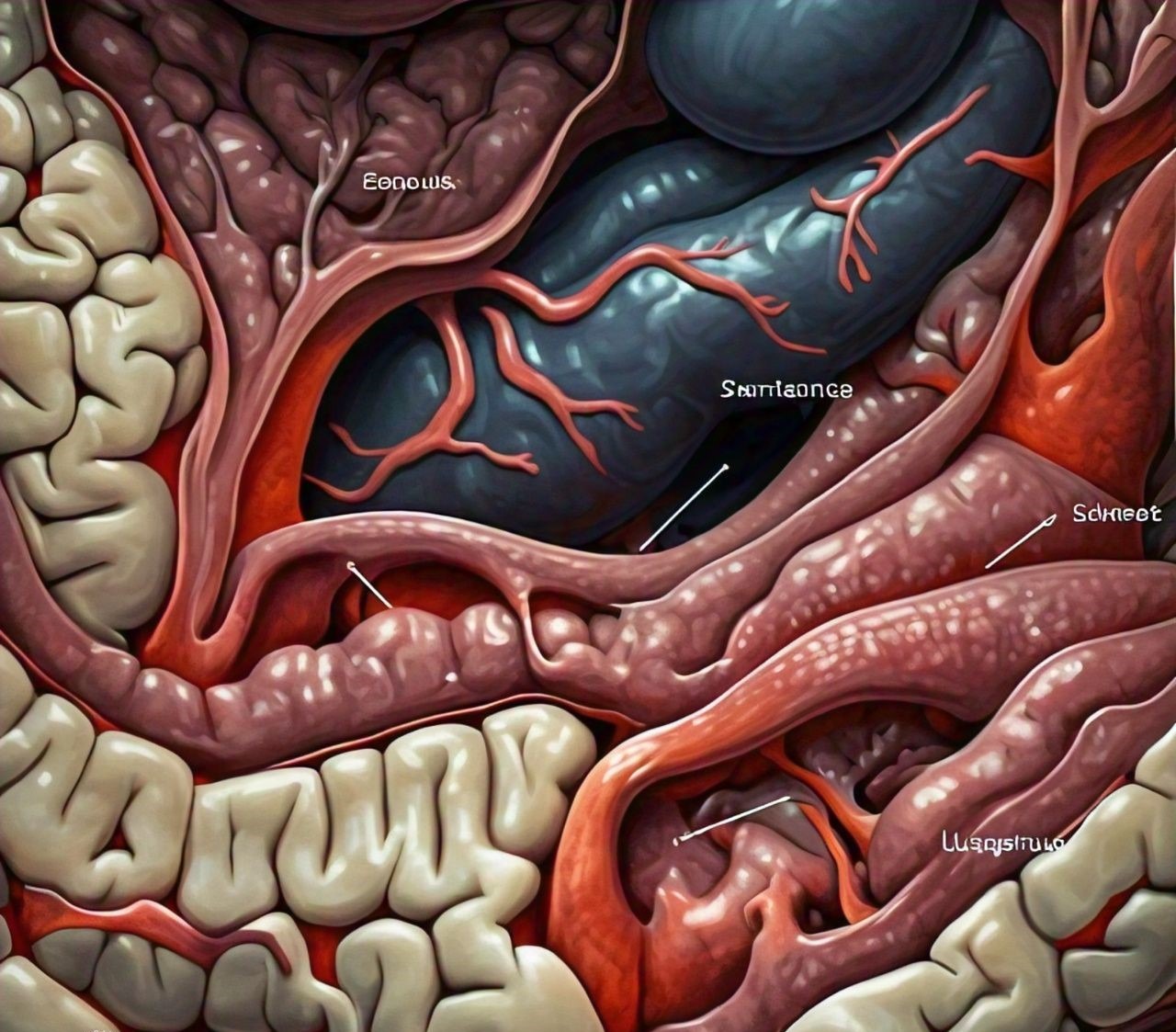
This condition happens because of a misfire in the immune system that triggers ongoing inflammation along the digestive tract. Crohn’s can affect any part of the gastrointestinal (GI) system, from mouth to anus, though it commonly impacts the small intestine and colon. This sets it apart from other conditions like ulcerative colitis, which sticks to the colon.
What Causes Crohn’s Disease?
While no one knows exactly what triggers Crohn’s disease, researchers think it’s tied to a mix of things:
- Genetics: If someone in your family has it, you’re at a higher risk.
- Immune System Issues: The immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, sparking inflammation.
- Environmental Triggers: Factors like stress, certain foods, and smoking might lead to flare-ups.
Who’s More Likely to Get Crohn’s?
Some groups of people face a higher risk, including:
- Young Adults: It often starts in adolescence or early adulthood.
- Certain Ethnicities: People of Eastern European Jewish descent (Ashkenazi) tend to get it more.
- Family History: Having relatives with Crohn’s ups your risk a lot.
- Smokers: Smoking doesn’t help—it can actually make symptoms worse.
What Are the Symptoms?
Symptoms vary depending on where the inflammation is and how bad it gets. Most commonly, people with Crohn’s deal with:
- Persistent diarrhea
- Stomach pain or cramps
- Blood in their stool
- Extreme tiredness
- Weight loss and low appetite
Some also experience fever, joint pain, and skin problems that go along with the disease.
How is Crohn’s Disease Diagnosed?
Doctors typically use a combination of methods to diagnose Crohn’s:
- Colonoscopy: A camera checks for inflammation in the colon.
- Endoscopy: Like a colonoscopy, but for the upper GI tract.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the digestive system.
- Blood Tests: Measures inflammation markers often seen with Crohn’s.
Catching Crohn’s early makes it easier to manage and reduces the risk of complications.
Complications from Crohn’s
Without proper treatment, Crohn’s can lead to serious complications like:
- Intestinal Blockages: Scar tissue can narrow the intestines, causing blockages.
- Fistulas: These are abnormal connections between parts of the intestine or other organs, leading to infections.
- Malnutrition: Crohn’s makes it hard for your body to absorb essential nutrients.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with Crohn’s can be exhausting. The constant need for restroom breaks, combined with pain and fatigue, can make work and social life challenging. Many people with Crohn’s also struggle with anxiety or depression because of these daily disruptions.
How is Crohn’s Treated?
Though there’s no cure, several treatments help manage symptoms and aim for remission (when symptoms are low or gone):
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: First-line treatments that reduce inflammation.
- Immune Suppressors: These medications slow down the immune system’s overreaction.
- Biologics: They target specific proteins involved in the inflammation process.
- Surgery: Sometimes, damaged parts of the intestines need to be removed.
New Research on Crohn’s Disease
A recent study suggests that the gut microbiome, the bacteria living in your intestines, plays a key role in Crohn’s disease. Researchers discovered that people with Crohn’s have a very different set of gut bacteria compared to those without the disease. This imbalance might be the culprit behind the disease’s onset and progression.
The study also highlights promising treatments like probiotics and fecal microbiota transplants (FMT), which could restore a healthy balance in the gut and help patients find relief from their symptoms.
Diet and Lifestyle Tips for Managing Crohn’s
Diet can make a big difference for people with Crohn’s. While there’s no one-size-fits-all solution, some common approaches include:
- Low Residue Diet: Reducing high-fiber foods to give the gut a break.
- Gluten-Free Diet: Some patients feel better after avoiding gluten.
- FODMAP Diet: Cutting down on hard-to-digest carbohydrates that trigger symptoms.
Foods to avoid? Dairy, high-fat meals, and raw veggies (especially during flare-ups). Keeping a food diary can help you figure out which foods make things worse.
On the lifestyle side, managing stress is key since it can trigger flare-ups. Techniques like meditation or yoga can help. Regular, low-impact exercise like swimming or walking can also improve your overall health and keep inflammation down.
Crohn’s Disease in Children and Young Adults
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease can affect children and young adults, presenting additional challenges. In children, Crohn’s disease can stunt growth and delay puberty. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for minimizing long-term effects of Crohn’s disease in children.
Managing Crohn’s Disease in Adolescents
Teens with Crohn’s disease may face difficulties in managing the disease alongside school and social life. Education and a strong support network are crucial for adolescents living with Crohn’s disease
Conclusion
Crohn’s Disease is a lifelong condition that requires careful management and ongoing monitoring. While there is no cure yet, advances in research have introduced new treatments and therapies that provide hope for those living with the disease. Understanding its symptoms, triggers, and treatment options is crucial in managing the impact it has on daily life. Through a combination of medication, diet changes, and stress management, many people with Crohn’s Disease are able to lead fulfilling lives. Staying informed about the latest studies and breakthroughs is key to navigating the challenges posed by this complex condition.
For more information on fitness and health, check out these resources:
Explore more articles on our site:
- How to Increase Running Stamina for Beginners at Home
- What Happens if You Don’t Get Enough Sleep Consistently: Effects and Solutions
- The Ultimate Guide to Healthy Living in 2024
- The Future of Artificial Intelligence: What to Expect
- Unlocking the Potential of Chat GPT Software: Revolutionizing AI Conversations
- Best Sleeping Position for Peripheral Artery Disease [New 2024]
- How to Increase Running Stamina for Beginners at Home
- 5 New Inner Thigh Exercises for Men and Women